利用nanoscope模块可以快速地将AFM成像原始数据转换为便于后续自己写代码分析的数据类型。
安装 nanoscope 模块可以使用 pip install nanoscope 命令即可。
然后这个模块附带了示例数据和代码,可以到该模块的安装目录中找到。
{anaconda3}\envs{afm}\Lib\site-packages\nanoscope
{anaconda3} 是 anaconda3 的安装目录, {afm} 是我创建的专门用于AFM成像数据分析的python虚拟环境
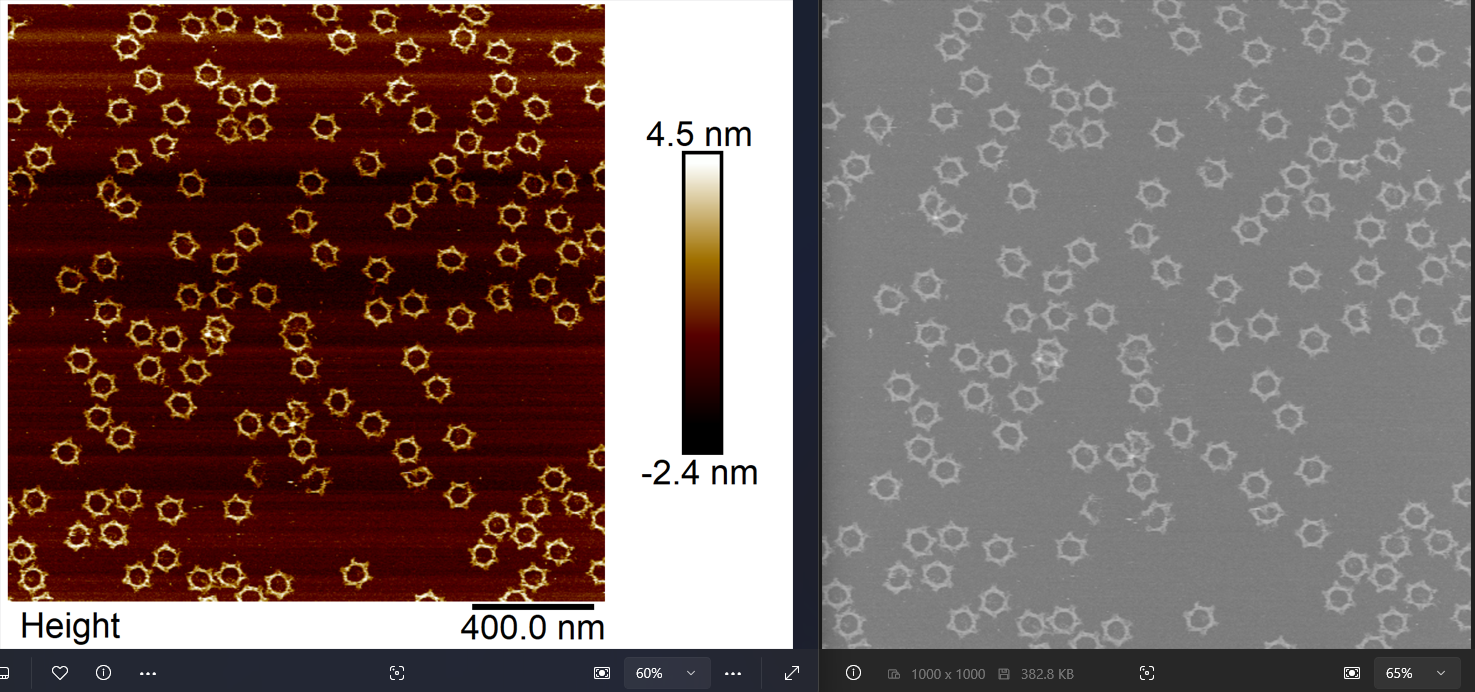
实际上这个部分内容要完成对AFM成像数据的预处理并导出为8-bit灰度图,具体效果如上。
获取高度数据的基础函数我已经封装如下:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
def getHeightData(fp):
from nanoscope import files
from nanoscope.constants import METRIC
data = {}
with files.ImageFile(fp) as f:
height = f[0] #默认AFM成像第一个通道就是height
image, ax_properties = height.create_image(METRIC)
assert ax_properties['title']=='Height'
data['data'] = image
data['aspect_ratio'] = height.aspect_ratio
data['scan_size'] = height.scan_size
data['scan_size_unit'] = height.scan_size_unit
data['z_sens_units'] = height.z_sens_units
return data 这里面 .create_image 是 nanoscope 模块自带的方法把最原始的数值转换为了高度,高度的单位可以查看 z_sens_units,然后创建的 image,每一条 row 就是 AFM针尖扫描的 line,然后每条 line 上采样多少 number就对应了图像的 col。所以 scan_size 就对应着 x_range。然后根据 aspect_ratio(横纵比,一般为1) 可以计算 y_range。
由于实际采集样品数据的类型比较单一(一般是正方形,扫描区域通常是微米级别,高度是纳米级别,可统一单位到纳米),所以进一步简化这个函数,避免各种单位判断和比例转换。
def getHeightData(fp):
from nanoscope import files
from nanoscope.constants import METRIC
data = {}
with files.ImageFile(fp) as f:
height = f[0]
image, ax_properties = height.create_image(METRIC)
assert ax_properties['title']=='Height'
assert abs(height.aspect_ratio-1)<0.01
assert height.z_sens_units=='nm'
assert height.scan_size_unit==r'µm'
data['data'] = image[::-1]
# y axis invert,保持和在 NanoscopeAnalysis中看到的效果一样
data['row'], data['col'] = image.shape
data['pixelsize'] = height.scan_size*1000/data['row']
return data 需要注意的是,此时得到的高度数据没有对齐基线,所以还需要进行 flatten 处理。这里提供了两种方法。一个是 median 中值对齐方法,适用于视野中样品颗粒较低的情况。一种是 polyfit 对齐方法,一般情况下都能获得不错的抚平效果。
def flat_median(arr):
box = []
for line in arr:
line_ = line - np.median(line)
box.append(line_)
box = np.array(box)
return box
def flat_polyfit(arr, order=1):
box = []
for line in arr:
coeff = np.polyfit(range(len(line)),
line,
order)
correction = np.array(
[sum([pow(i, n) * c
for n, c in enumerate(reversed(coeff))])
for i in range(len(line))])
line_ = line - correction
box.append(line_)
box = np.array(box)
return box完成 AFM 高度数据的抚平之后,为了导出为图像,还需要一些工作,主要涉及高度数据到 8-bit 像素的映射,以及导出图像的 pixelsize有一个 rescale 的过程。具体函数代码如下:
def convert(hmap, z_range=[-10, 10]):
data = hmap.copy()
low, high = z_range
data = (data - low)/(high - low)
inds = np.where(data<0)
data[inds] = 0
inds = np.where(data>1)
data[inds] = 1
data = data*255
data = data.astype('uint8')
return data
def resize(data, pixelsize=2):
# resize image, 1 pixel = 2 nm
image = data['convert_flat_data']
img = Image.fromarray(image)
pixelsize0 = data["pixelsize"]
width = data["col"]
height = data["row"]
w = int(width*pixelsize0/pixelsize)
h = int(height*pixelsize0/pixelsize)
img2 = img.resize((w,h))
data['export_image'] = img2
data["export_image_pixelsize"] = pixelsize
return data注意在这个地方,我根据实际情况,将高度映射的区间定到了 -10 到 10 nm,然后导出图像的 pixelsize 设置为了 1 pixel = 2 nm。
基于上述函数,对于单个AFM成像的原始数据,其预处理和导出函数再集成封装一下,就变成这样:
def single(fp, flat='median', pixelsize=2, z_range=[-10, 10]):
assert fp.endswith(".spm")
# 目前仅对Bruker Multimode VIII的采集到的spm数据文件进行过测试
# 发现部分以 `.001`, `.002` 之类结尾的数据不能nanoscope模块不能正确解析
# 后续可尝试另外一个 nanoscope 的开源项目以获得更好的兼容性
# https://github.com/jmarini/nanoscope/
data = getHeightData(fp)
if flat=='polyfit':
data['flat_data'] = flat_polyfit(data['data'])
else:
data['flat_data'] = flat_median(data['data'])
data['convert_flat_data'] = convert(data['flat_data'],
z_range=z_range)
data = resize(data, pixelsize=pixelsize)
fp2 = fp+".png"
data['export_image'].save(fp2)
return data如果是要对比较多的数据文件进行批量处理,可以考虑使用 joblib 模块来并行:
from glob import glob
from joblib import Parallel, delayed
fps = glob("*.spm")
# 获取所有 spm 文件列表
flat_method='median'
pixelsize=2
z_range=[-10, 10]
res = Parallel(n_jobs=-1)\
(delayed(single)(fp, flat_method, pixelsize, z_range)\
for idx,fp in enumerate(fps))
此处评论已关闭